Latest Trends in Cell Research: Revolutionizing Medicine and Biotechnology
Cell research continues to be at the heart of groundbreaking advancements in medicine, biotechnology, and regenerative therapies. As new technologies and techniques emerge, they offer scientists unprecedented insight into cellular functions, leading to potential breakthroughs in various fields including cancer research, gene therapy, and tissue engineering. In this blog, we explore some of the latest hot topics in cell research.
1. CRISPR-Cas9 and Gene Editing: Transforming Genetic Research
The CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing technology has revolutionized the field of molecular biology. This system, initially discovered in bacteria as a defense mechanism, allows scientists to make precise edits to the genome. Researchers are now using CRISPR to study gene function, correct genetic disorders, and even develop potential therapies for diseases such as sickle cell anemia, muscular dystrophy, and cystic fibrosis.
Recent advancements in CRISPR technology have enhanced its accuracy and reduced off-target effects, making it a powerful tool for both basic research and clinical applications. One of the most exciting developments is the use of CRISPR in somatic cell genome editing—directly modifying the DNA of adult cells to treat genetic disorders, without the need for germline modifications (Doudna & Charpentier, 2020).
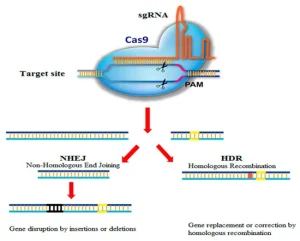
Figure 1. Schematic of CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing system.
2. Stem Cell Research: Unlocking Regenerative Medicine
Stem cells, particularly pluripotent stem cells, remain one of the most promising areas in cell research. These cells can differentiate into virtually any cell type, making them invaluable for regenerative medicine. The potential for stem cells to treat degenerative diseases, such as Parkinson’s disease, heart disease, and spinal cord injuries, is vast.
The latest research focuses on induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), which are adult cells reprogrammed to an embryonic-like state. iPSCs have opened doors to personalized medicine, where patients’ own cells can be used to generate tissue for transplantation or to study diseases in the lab.
New techniques in 3D cell culture systems, which allow stem cells to grow in environments that mimic human tissues more closely than traditional 2D cultures, are also pushing the field forward. These systems have improved our understanding of how stem cells interact with their environment and may enhance their therapeutic applications (Liu et al., 2021).
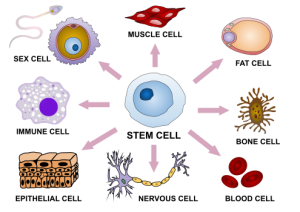
Figure 2. Stem cell differentiation into various animal tissue types
3. Cancer Immunotherapy: Using Cells to Fight Cancer
Cancer immunotherapy, a treatment strategy that harnesses the body’s immune system to fight cancer, has become one of the most promising therapeutic approaches in oncology. A key component of immunotherapy involves the use of chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy, where a patient’s T-cells are genetically modified to target cancer cells more effectively.
CAR-T cells have shown great success in treating hematologic cancers like leukemia and lymphoma, and researchers are now working to extend this technology to solid tumors. The ongoing challenge is to improve the efficacy of CAR-T therapies in treating solid cancers and reduce the risk of severe side effects such as cytokine release syndrome (Ghorashian et al., 2020).
4. Organoids and 3D Cell Culture: Modeling Human Diseases
Organoids are 3D cellular structures that mimic the architecture and function of real organs. Researchers are increasingly using organoids to model diseases and test drug responses. These miniature organ models are derived from stem cells and can replicate the functionality of the organs from which they are derived.
Organoids are being used to study a variety of diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and infectious diseases. For example, researchers have created brain organoids to study neurological diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. These models offer insights into disease mechanisms and provide a more accurate platform for drug testing compared to traditional 2D cell cultures (Lancaster et al., 2020).
5. Cell Therapy for Autoimmune Diseases
Cell-based therapies are showing great promise in treating autoimmune diseases, where the body’s immune system attacks its own tissues. Recent studies have focused on regulatory T-cell (Treg) therapy, where patients are treated with a specific subset of T-cells that regulate the immune response.
For diseases like type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and rheumatoid arthritis, Treg-based therapies could help rebalance the immune system, reducing inflammation and tissue damage. Ongoing clinical trials aim to refine these therapies and bring them closer to clinical use (Mori et al., 2021).
Conclusion
The field of cell research is advancing at an unprecedented pace, with exciting new technologies like CRISPR and stem cells revolutionizing medicine and biotechnology. From cancer immunotherapies to regenerative medicine, these innovations are not only reshaping our understanding of human biology but also paving the way for novel treatments that were once thought to be unattainable.
With these cutting-edge advancements, we are closer than ever to addressing some of the most challenging medical issues of our time. As research progresses, we can expect even more breakthroughs that will continue to shape the future of healthcare and improve the quality of life for millions of people worldwide.
- Doudna, J. A., & Charpentier, E. (2020). The new frontier of gene editing with CRISPR-Cas9. Nature Biotechnology, 38(5), 614-624.
- Liu, X., et al. (2021). Advancements in stem cell research and regenerative medicine. Stem Cells Translational Medicine, 10(4), 456-468.
- Ghorashian, S., et al. (2020). CAR-T therapy in cancer treatment: Challenges and opportunities. Cancer Cell, 37(4), 456-464.
- Lancaster, M. A., et al. (2020). Organogenesis in a dish: Modeling human diseases with 3D organoids. Trends in Cell Biology, 30(10), 792-805.
- Mori, F., et al. (2021). Regulatory T-cell therapy for autoimmune diseases: New frontiers in cell-based therapy. Nature Reviews Immunology, 21(6), 409-421.